BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
Overview
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a dynamic routing protocol that facilitates the exchange of routing information between network hosts across autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. Each AS is uniquely identified by an Autonomous System Number (ASN), which is used in packet exchanges across networks. BGP can be used for both Wide Area Network (WAN) or exterior routing (eBGP) and Local Area Network (LAN) or interior routing (iBGP).
Functionality
In AmZetta’s zWAN, BGP is used to establish peering between the Edge Controller and the ISP. An ASN is required to configure BGP; this can be obtained from ARIN or an equivalent organization based on geographic location for eBGP or agreed upon internally for iBGP.
Multiple ISPs can be configured as BGP neighbors, allowing the Edge Controller to peer with multiple providers. When BGP peering is established with an ISP, the Edge Controller can advertise local address spaces to the ISP. ISPs can then return a default route, a partial routing table, or a complete Internet routing table. Configuring for a default route requires minimal system resources.
For a deeper understanding of BGP configuration parameters, refer to the official FRR documentation at FRR BGP Documentation.
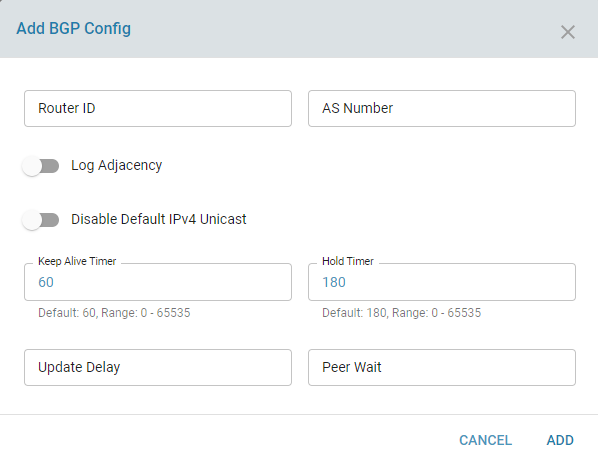
Configuration Parameters
To enable BGP functionality:
-
- Ensure that the BGP service is set to the enabled state.
- Specify an ASN and a unique router ID. The router ID is typically set to a local private IP address.
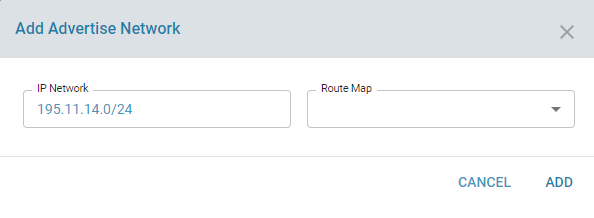
Advertise Local Networks
The “Advertise Network” option allows you to announce local networks to peers.
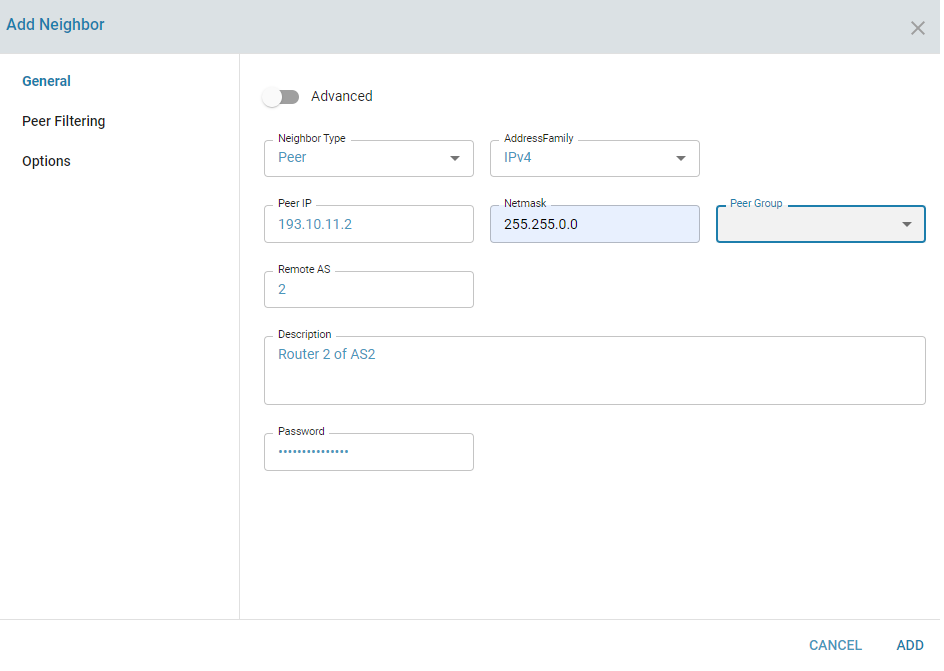
Peering with an ISP
To establish peering, configure each ISP as a BGP Neighbor.
Use Cases
- Configure BGP peering with multiple neighbors for bidirectional route advertisement and exchange.
- Testing for BGP functionality is available within the deployment framework:
- Scripts can be provided by the AmZetta Support Team upon request.
- These tests are based on “netkit-labs_interdomain-routing.tar” from Netkit Labs. The tar file is included in the corresponding folder.
Known Limitations
No known limitations at this time.