-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zTC
-
- Articles coming soon
-
StorTrends
VLAN
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
Overview
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) address the growing complexity of networks by allowing organizations to scale and segment their networks, enhancing security and reducing latency. Traditionally, a LAN connected devices within a single physical location via Ethernet, but VLANs now enable these connections virtually across multiple LAN segments.
VLANs help manage network traffic, reduce collision rates, and improve network efficiency by creating isolated broadcast domains. Devices in a VLAN act as though they’re on a single LAN, even if spread across different physical segments, making VLANs ideal for flexible network configurations and enhanced data security.
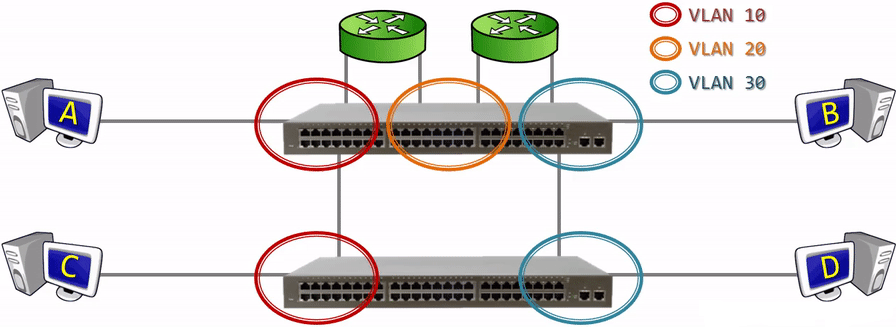
Key Features of VLANs
- Network Segmentation: Reduces network congestion and limits broadcast domains.
- Improved Security: Isolates sensitive data flows within segments.
- Logical Partitioning: Allows grouping based on roles or departments rather than physical locations.
Functionality
zWAN’s VLAN feature enables users to create and manage VLANs on a single interface, with each VLAN identified by a unique tag. Key functionalities include:
- Add VLAN: Create a VLAN by assigning a unique tag ID and description.
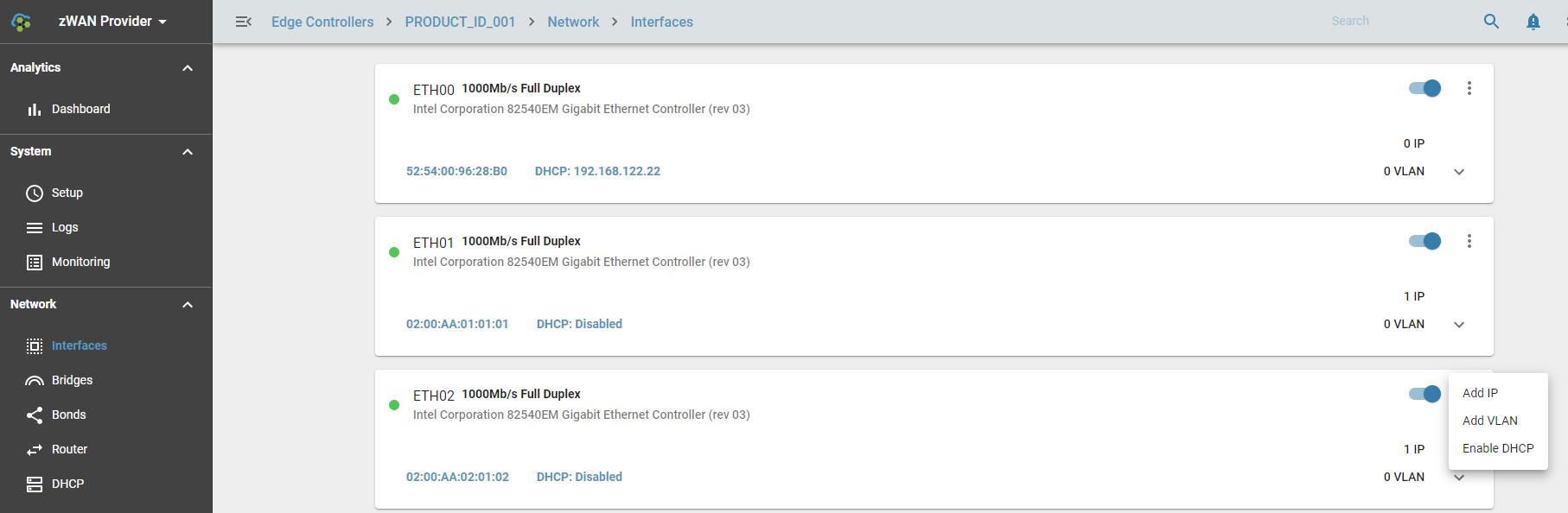
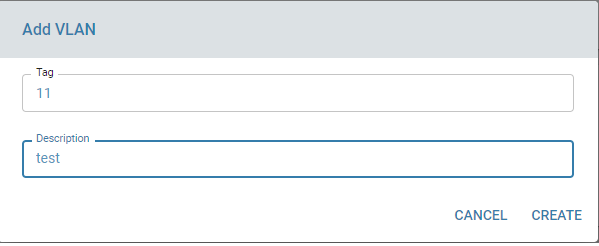
- Edit/Modify VLAN: Change the description of an existing VLAN.
- Delete VLAN: Remove existing VLANs as needed.
- Set Static IP for VLAN: Assign a static IP address to a VLAN, similar to adding an IP to an interface.
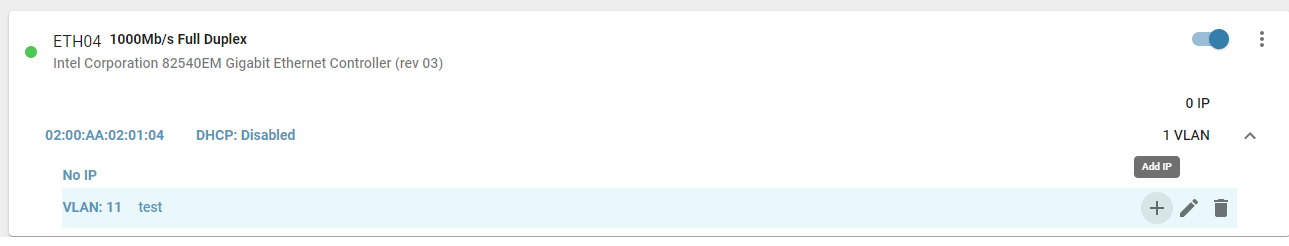
- Edit/Modify Static IP of VLAN: Update the IP as needed.
- Delete Static IP of VLAN: Remove IP assignments for VLANs.
Configuration Parameters
- VLAN Tag ID: Range 1-4094
- Description: Brief identifier for each VLAN
- Static IP Address: Manually assigned IP for VLANs
- Netmask: Associated netmask for the static IP
Result
Once a VLAN is created and assigned an IP, it appears in the interface section with its details displayed.
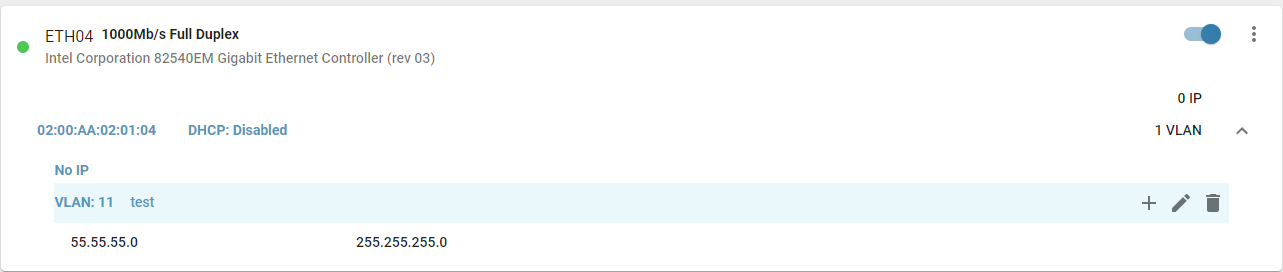
Using VLANs increases network performance, provides greater configuration flexibility, and reduces administrative efforts, especially in large organizations.
Use Cases
For example, placing interdepartmental teams (e.g., marketing, sales, IT, business analysts) on the same VLAN facilitates efficient data sharing and collaboration by streamlining network segmentation and enhancing teamwork.
Known Limitations
- DHCP IP Support: zWAN’s VLANs do not currently support dynamic IP assignment via DHCP.
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |