-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zTC
-
- Articles coming soon
-
StorTrends
-
zAccess
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
zGuardian
Net Balancer
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
Load Balancer
Overview
Traffic Steering is used when the router is configured with multiple internet connections or tunnels for purposes such as balancing outgoing LAN traffic, maintaining network redundancy, and managing faults across multiple lines. The LAN traffic is distributed using two weighted round-robin methods:
- Connection-Based Load Balancing: This is flow-based balancing, where each flow is assigned an outgoing interface and remains on that interface for its lifetime unless a failure is detected. This method is primarily used for WAN interfaces where NAT connections must be maintained for end-to-end communication.
- Packet-Based Load Balancing: In this method, each packet can be assigned to a different outgoing interface. It is used only with tunnels, as NAT is not involved.
Traffic can also be directed through a single interface. The detection of traffic is handled by the flow classifier module, which offers multiple ways of identifying traffic, such as 5-tuple analysis, nDPI, and Web Categories.
Functionality
It supports four traffic modes:
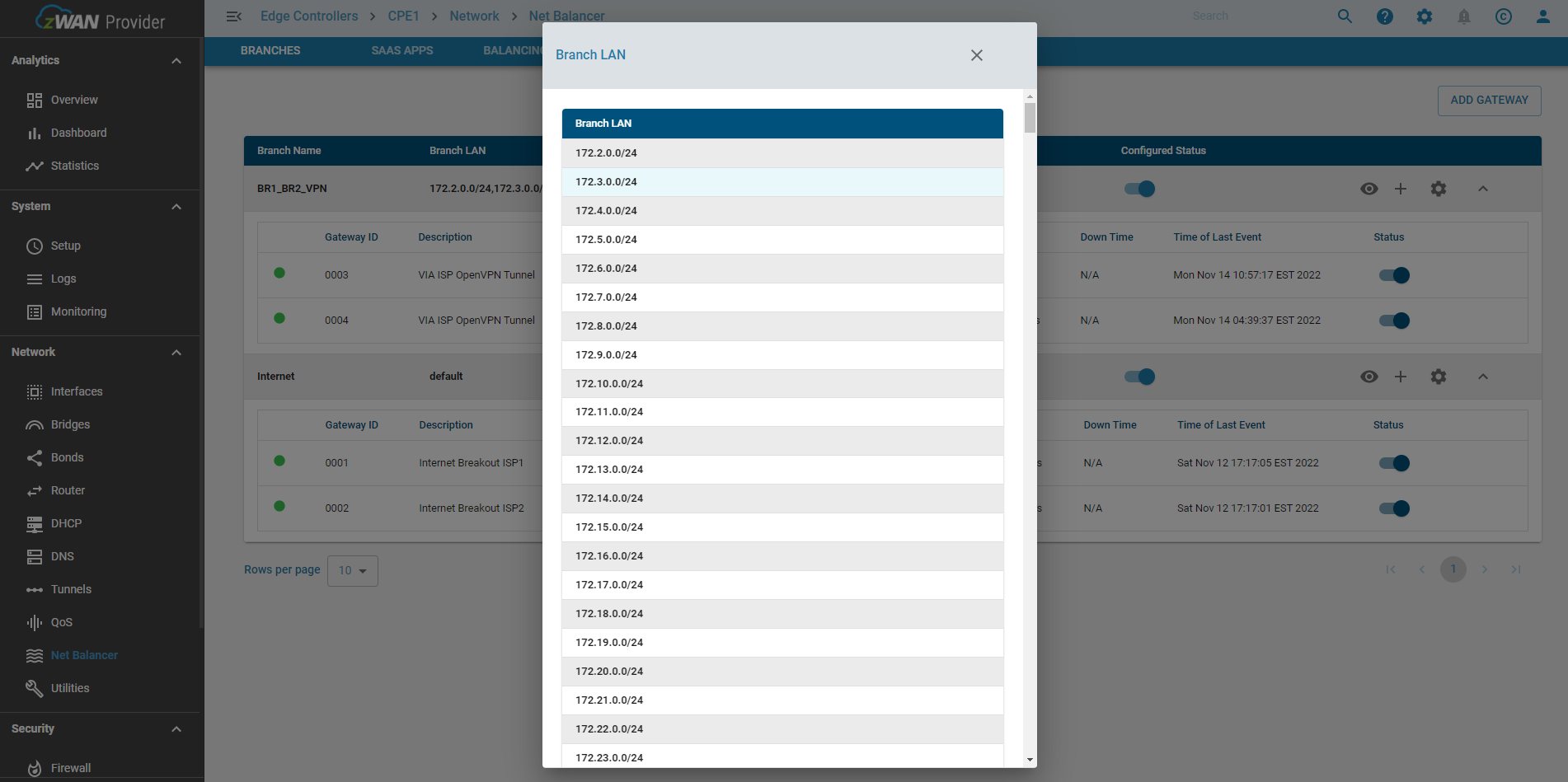
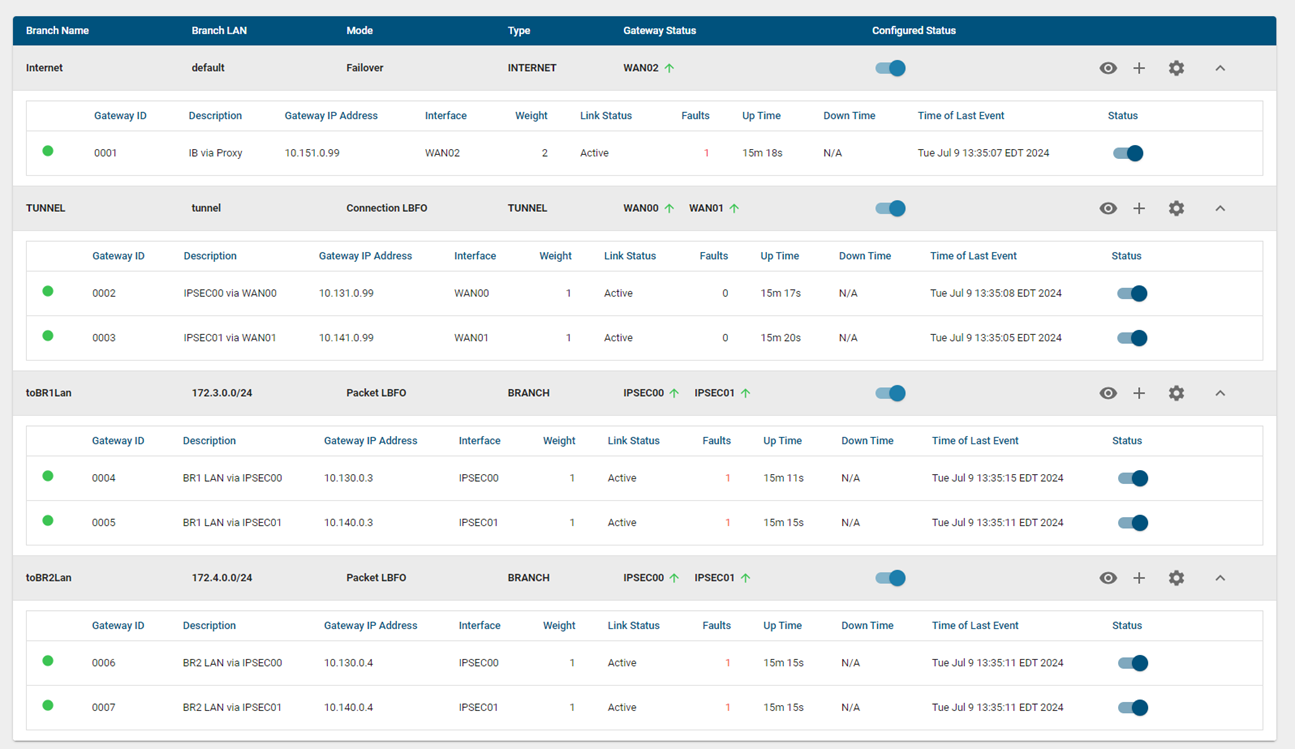
- Branch: Gateways can be grouped based on one or more LAN networks to form a separate load-balancing group. The LAN networks can be specified as a newline-separated file.
- Internet Breakout: Any traffic that does not belong to the branches or is internet-bound is forwarded to the default internet gateways.
- SAAS Breakout: When internet breakout traffic is directed toward the data center via tunnels, trusted traffic from SAAS applications (e.g., Microsoft Teams, Salesforce) can be sent directly to the internet via WAN interfaces.
- Tunnel Breakout: Used in scenarios where internet breakout traffic is directed toward the data center via tunnels. Tunnels are assigned to tunnel breakout gateways. It is also applicable when tunnel links use different WAN interfaces than the internet WAN interfaces.
Each load-balancing group can be configured in one of three modes:
- Load Balancing → Branch, Internet Breakout, SAAS Breakout & Tunnel Breakout
- Packet Balancing → Branch & Internet Breakout with tunnels
- Failover → Branch, Internet Breakout & SAAS Breakout
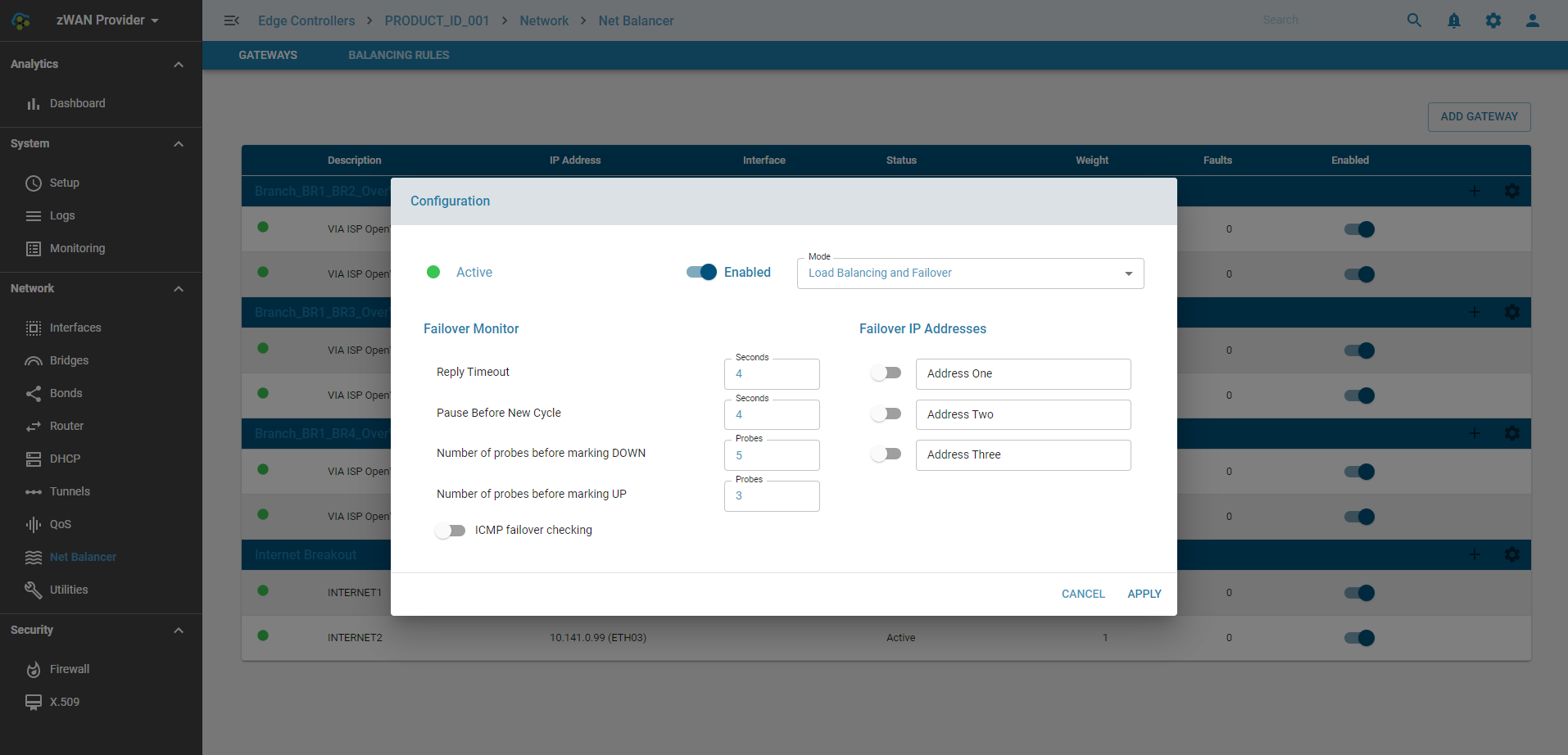
Gateway State Transition Parameters
Probes Before Marking DOWN:
- Defines the number of consecutive failed probe attempts before the gateway is marked as DOWN.
- Higher values lead to longer detection times.
- Lower values enable faster detection but may result in false alarms.
Probes Before Marking UP:
- Defines the number of consecutive successful probe attempts before the gateway is marked as UP.
- Higher values lead to longer recovery times.
- Lower values allow quicker recovery but may result in instability.
Pause Before New Cycle:
The time interval between each cycle of probe attempts.
Reply Timeout:
The maximum time allowed for a response from the gateway to each individual probe.
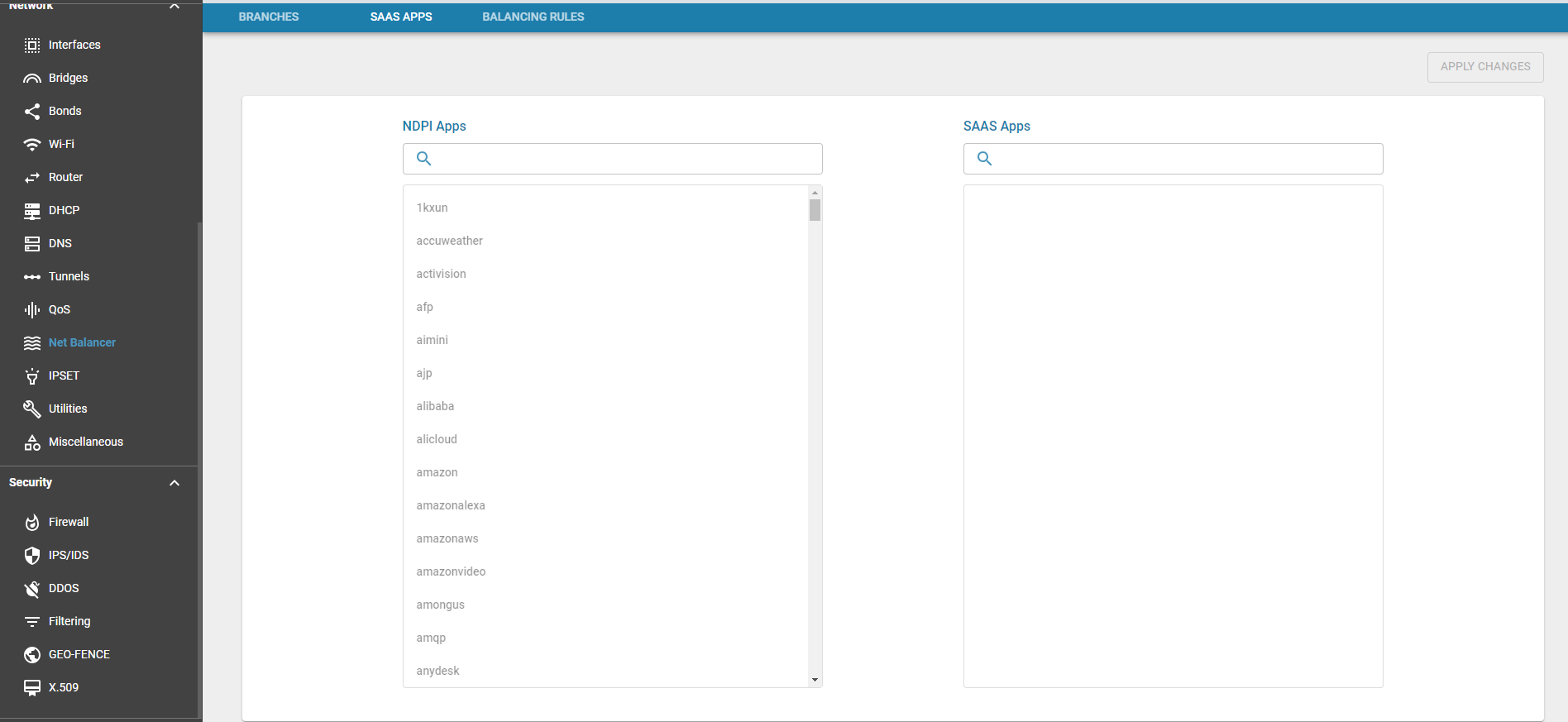
SAAS Breakout
SAAS applications can be configured via the SAAS Apps page. Users can specify which applications are trusted. Once configured, designated SAAS applications are routed through the SAAS breakout gateway.
Internet breakout and SAAS breakout can share the same interfaces. SAAS breakout can only be created using WAN-designated interfaces.
Configuration Parameters
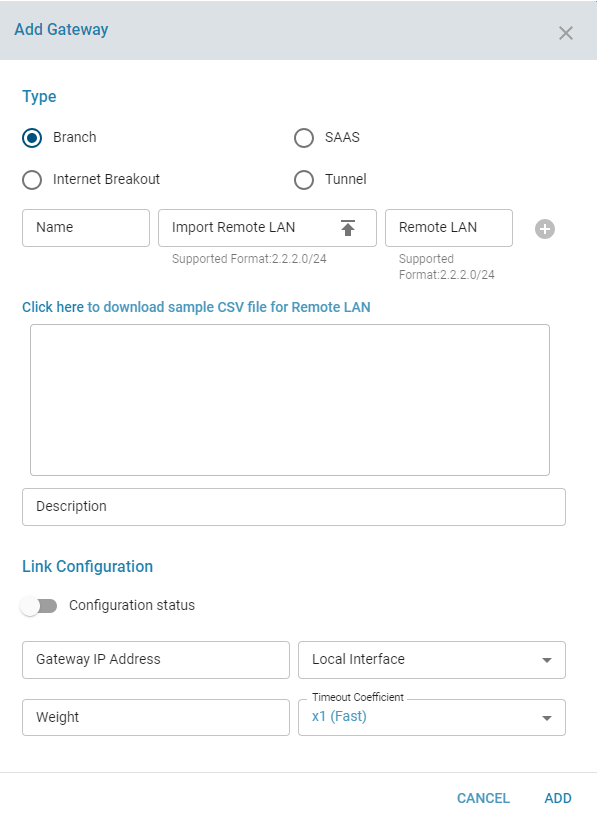
Add a Load Balancer Gateway
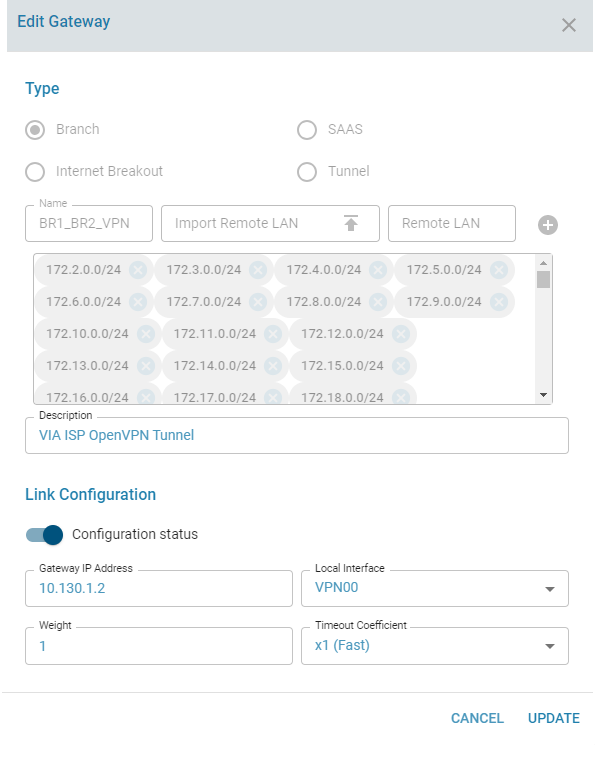
Edit a Load Balancer Gateway
View Branch Subnets
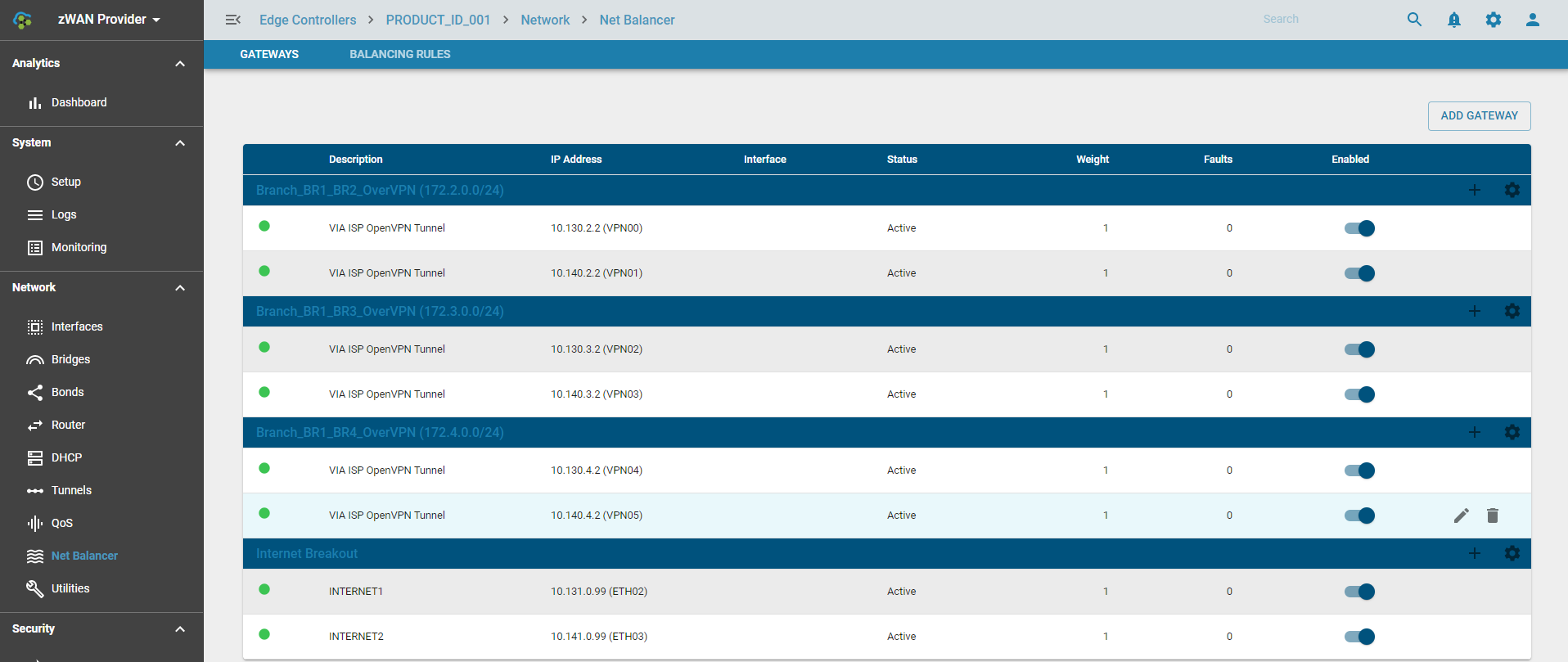
View Load Balancer Gateways
Configure the Load Balancer
Configure SAAS Apps
Tunnel Breakout Configuration
Advanced
For troubleshooting, if failures or routing updates are not acting correctly, the Load Balancer link monitor can be restarted. Please note this will result in a brief loss of branch and internet connectivity from the LAN. This is an alternative to rebooting the Edge Controller.
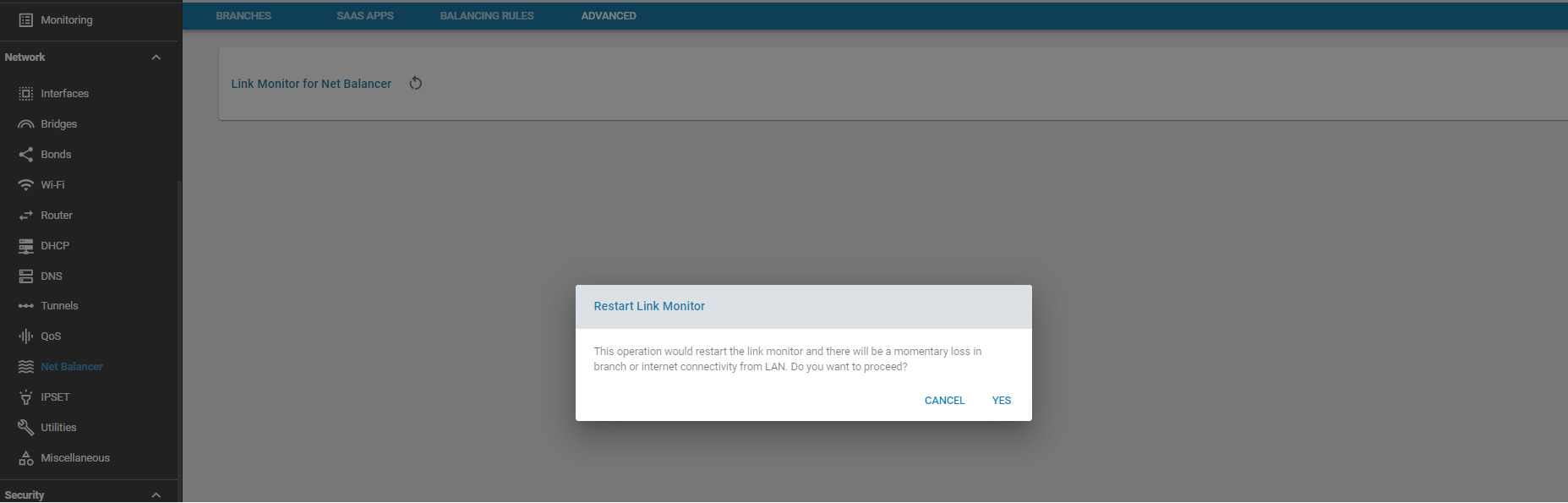
Use Cases
Classifying and directing traffic over dedicated links.
Known Limitations
- Editing the remote LAN is not supported.
- The number of supported gateways depends on the underlying hardware.
Future Enhancements
Further improvements to traffic steering and failover mechanisms.
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |