-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zTC
-
- Articles coming soon
-
StorTrends
-
zAccess
-
zGuardian
Flow Optimizer
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
Overview
The Flow Optimizer dynamically selects the best path for network traffic based on real-time performance metrics and configuration rules. Working in tandem with Traffic Steering and Flow Classification, it evaluates and adjusts paths to optimize flow according to line performance, path affinity, bandwidth availability, and cost factors.
Functionality
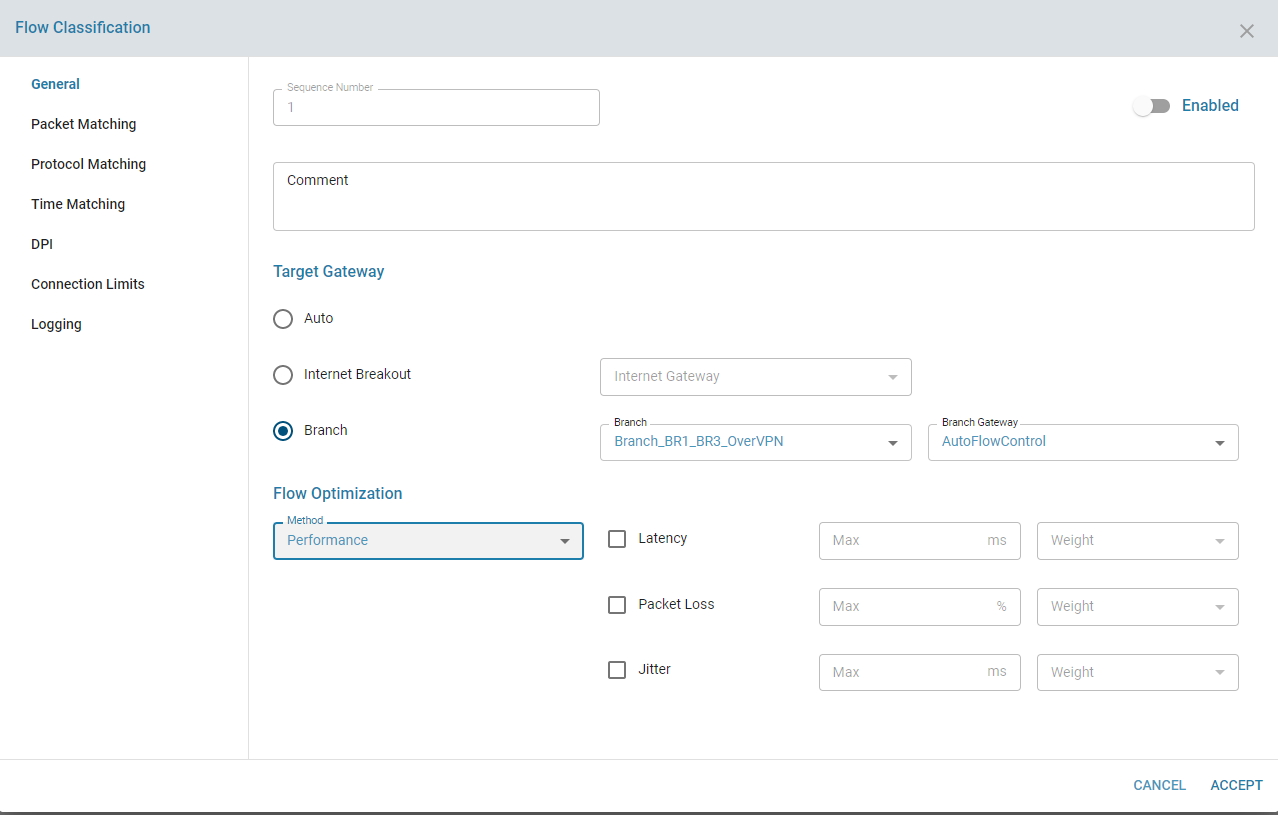
1. Line Performance
The Flow Optimizer monitors latency, jitter, and packet loss between endpoints (e.g., SSL VPN, IPsec tunnels, MPLS endpoints) using the TWAMP protocol. It ensures that each connection maintains quality by rerouting flows when performance thresholds are exceeded. When a threshold is surpassed, the optimizer seeks alternative paths within the load balancer’s connections to maintain high-quality service.
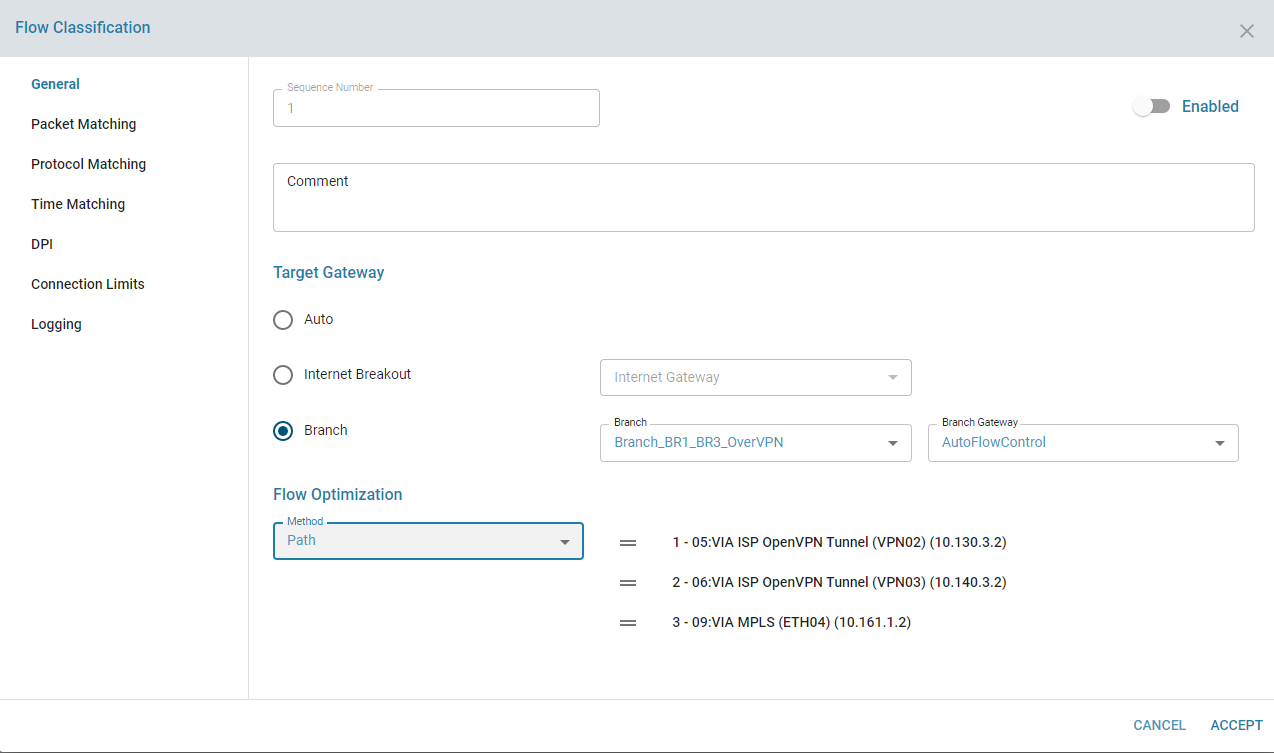
2. Path Affinity
Path preferences can be set for each flow. The Flow Optimizer follows the order of preferred paths, switching to alternate paths only if higher-priority ones are unavailable.
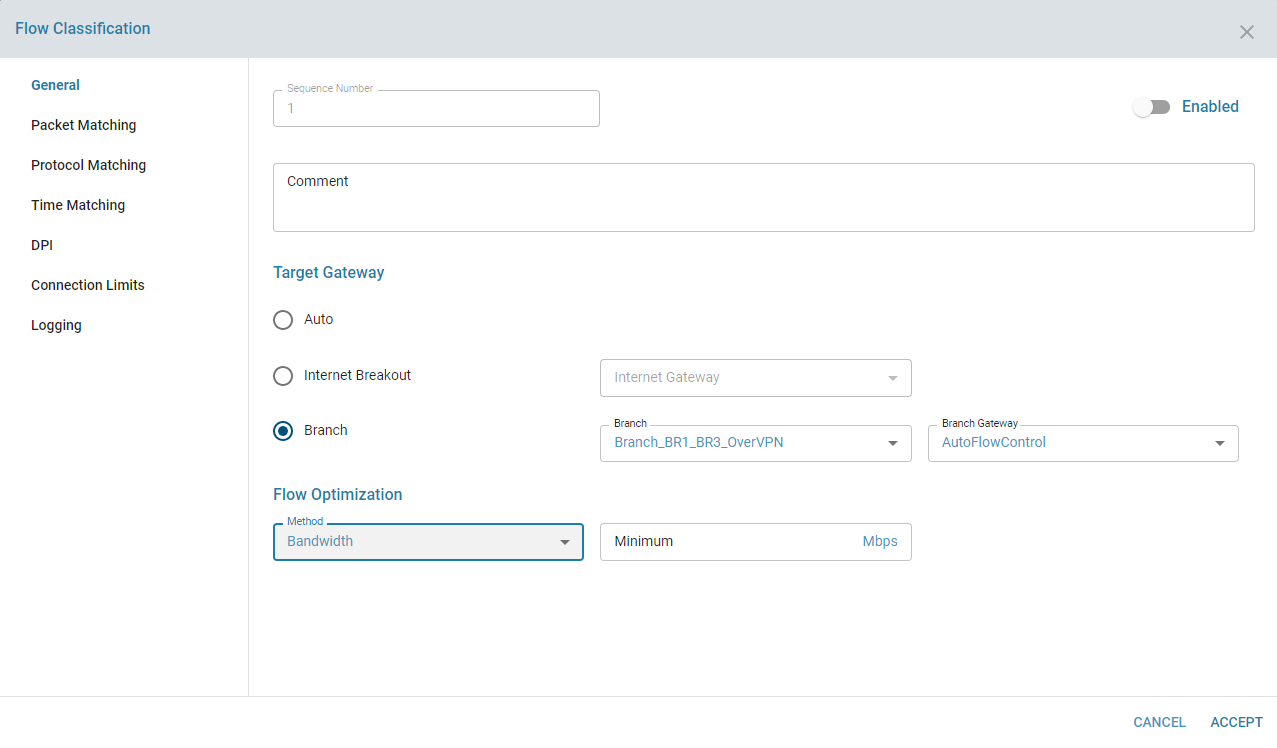
3. Bandwidth
The Flow Optimizer dynamically selects paths that satisfy each flow’s bandwidth requirements, switching paths as available bandwidth changes to ensure optimal performance.
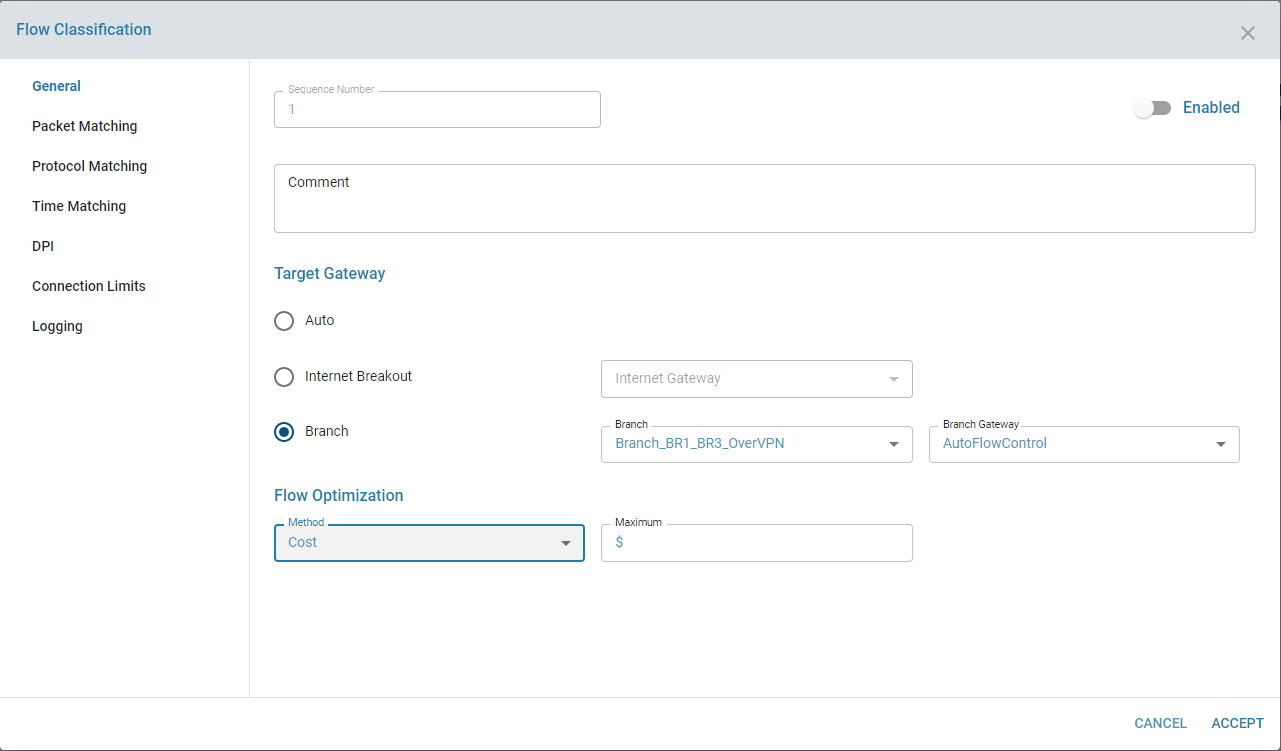
4. Cost
The optimizer can also adjust flow paths based on the cost of each connection, prioritizing paths according to cost-efficiency where configured.
System Behavior
Once rules and optimization parameters are set, the Orchestration Server will apply them, selecting optimal paths. The current network path (Gateway) for each flow is visible within the Balancing Rules section.
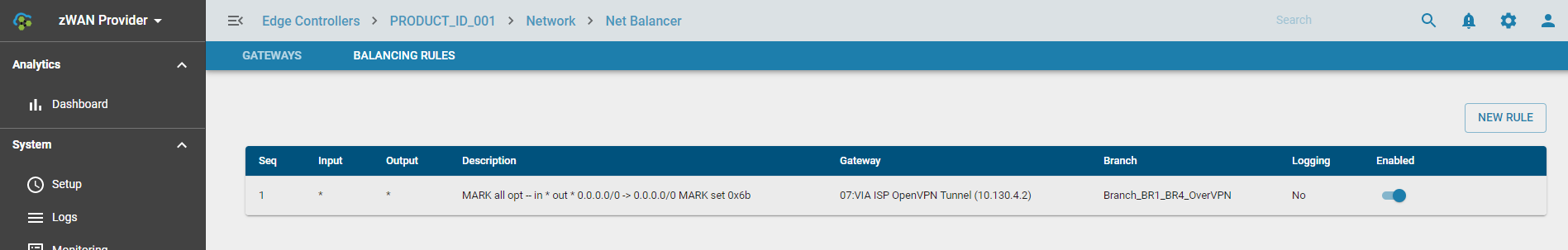
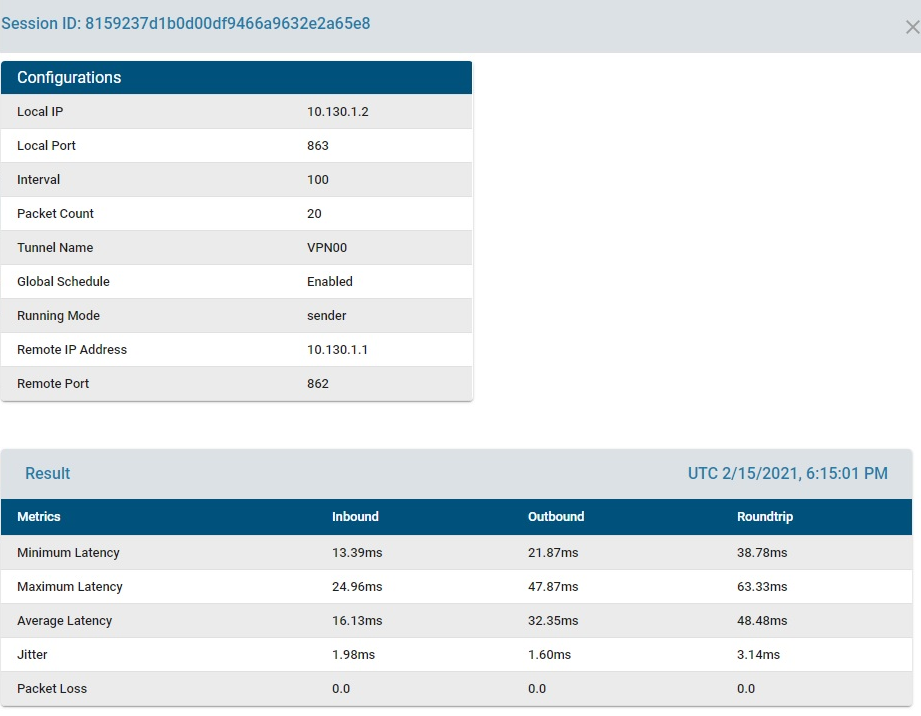
TWAMP Metrics for Decision-Making
The optimizer utilizes metrics such as average outbound latency, jitter, and packet loss to determine the best routing path.
Known Limitations
- Currently, only performance-based optimization is implemented.
- When multiple performance metrics are used, only the highest-weight metric is considered for path selection, potentially overlooking paths that meet all parameters.
- Bandwidth, cost, and path affinity-based optimizations are not yet implemented.
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |