-
SnapOS
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Citrix HDX + USB Headset (Call-Center Baseline)
- OS/Firmware Update & Rollback
- Power Management and Session State
- Wi-Fi Roaming & Link Change Mid-Session
- Kiosk / Assigned-Access Auto-Launch
- Barcode Scanner (HID) with Line-of-Business App
- Printing to Local USB & Network Printers
- USB Device Management – Block Storage
- Multi-Monitor & 4K Performance
- Microsoft AVD/RDP + Teams Optimized Video
- VMware Horizon + Smart Card / CAC Login
-
-
-
-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
- Firewall & Layer 7 Application Filtering
- VPN Site-to-Site Tunnel Setup & Connectivity (z40 to Cloud vGR)
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) / Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Testing
- DNS Filtering
- DDoS Protection & Logging
- MAC Address Filtering & Geo-fencing
- Application Control & Protocol Blocking
- Authentication & Access Control (zID)
-
- WAN Link Failover & Load Balancing (ACI Mode)
- Dynamic Path Selection & Application-Aware Routing
- SaaS & Internet Breakout Validation
- QoS for Microsoft Teams (Datacenter vGR + Branch z40)
- Tunnel Failover (z40 ↔ vGR) — WAN00 (wired) primary, WAN03 (4G) & WAN04 (5G) backups
- IP Routing & Static Route Steering (z40 Branch)
- VLAN & Layer-2 Bridging
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zGuardian
-
zAccess
-
StorTrends
IPv6
Setting Up IPv6 on AmZetta zWAN
Overview
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol, designed to address the limitations of IPv4. It introduces a 128-bit address space, ensuring a vast number of unique addresses. IPv6 also simplifies address management and reduces router processing overhead with more efficient headers.
Interface Configuration
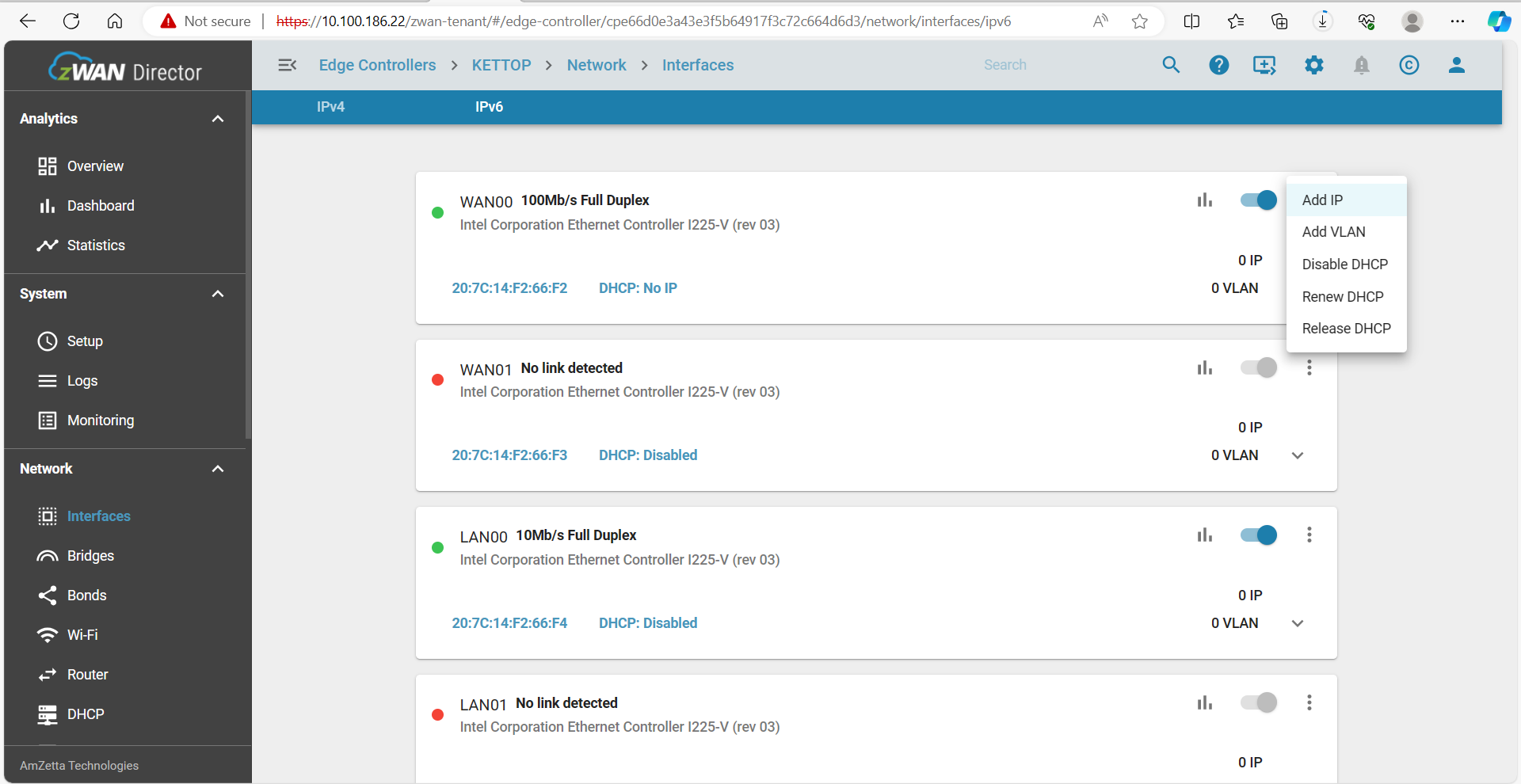
In zWAN, interfaces serve as the primary entry and exit points for network traffic. They are named as follows:
- ETH00, ETH01, ETH02 (Physical interfaces)
- VLAN Interfaces (Virtual interfaces)
LTE & WiFi Panels
Configurable Interface Features
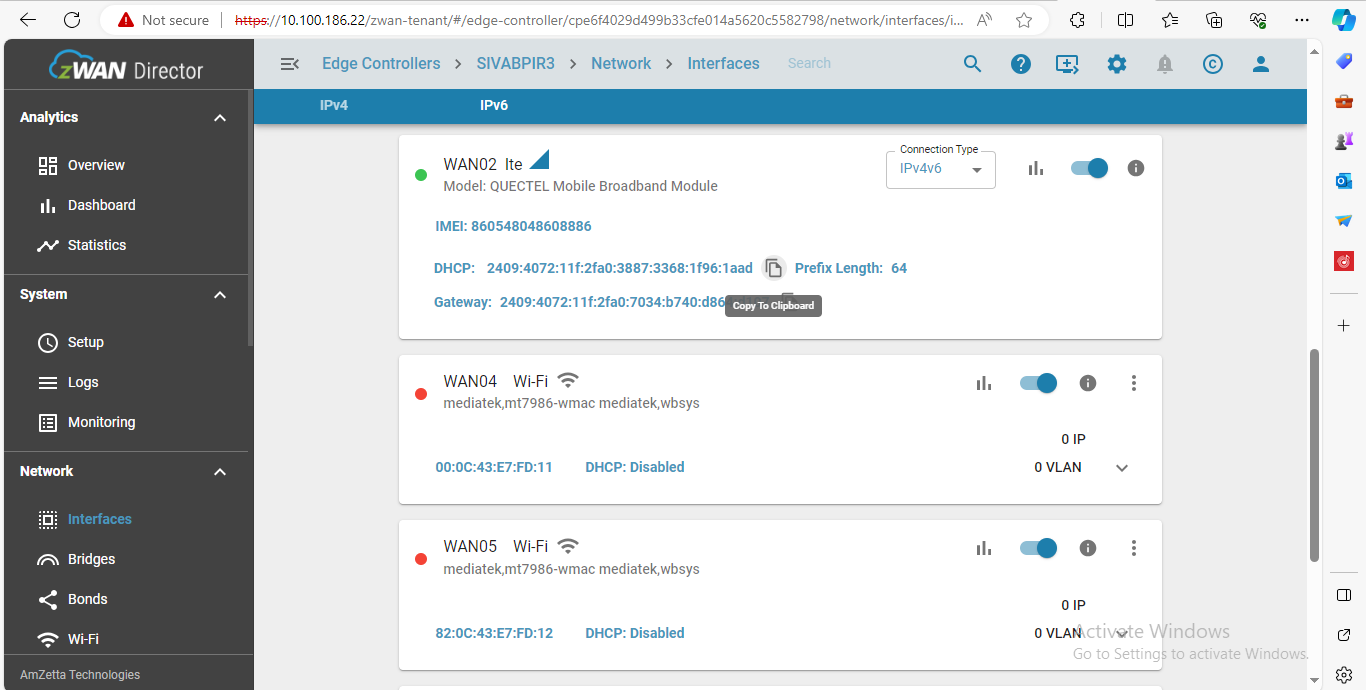
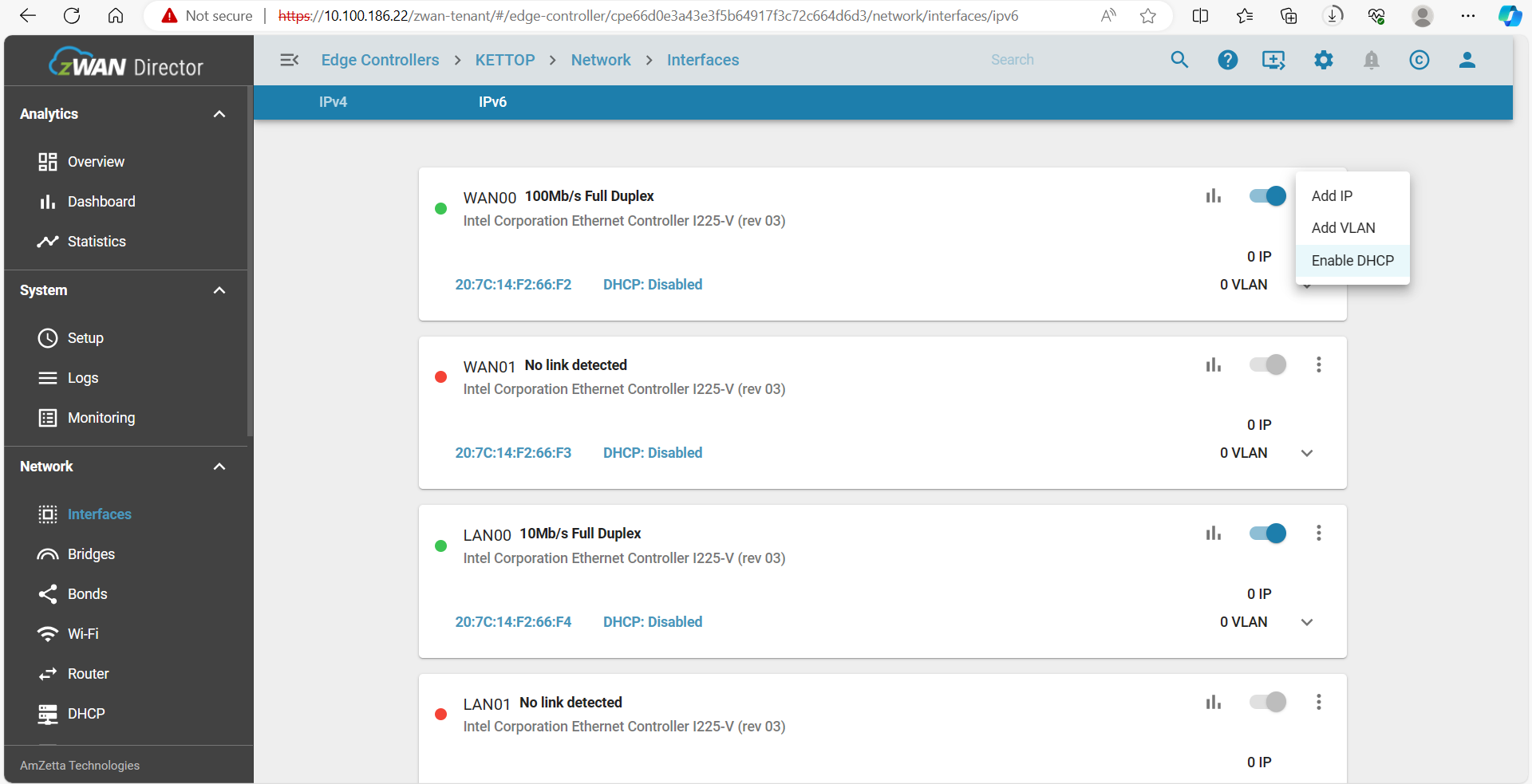
The following actions can be performed on zWAN interfaces:
- Assign a static IPv6 address
- Modify or remove a static IP
- Create VLANs on interfaces
- Assign static IPs to VLANs
- Obtain a DHCP-assigned IPv6 address
- Release or renew a DHCP-assigned address
- Enable or disable an interface
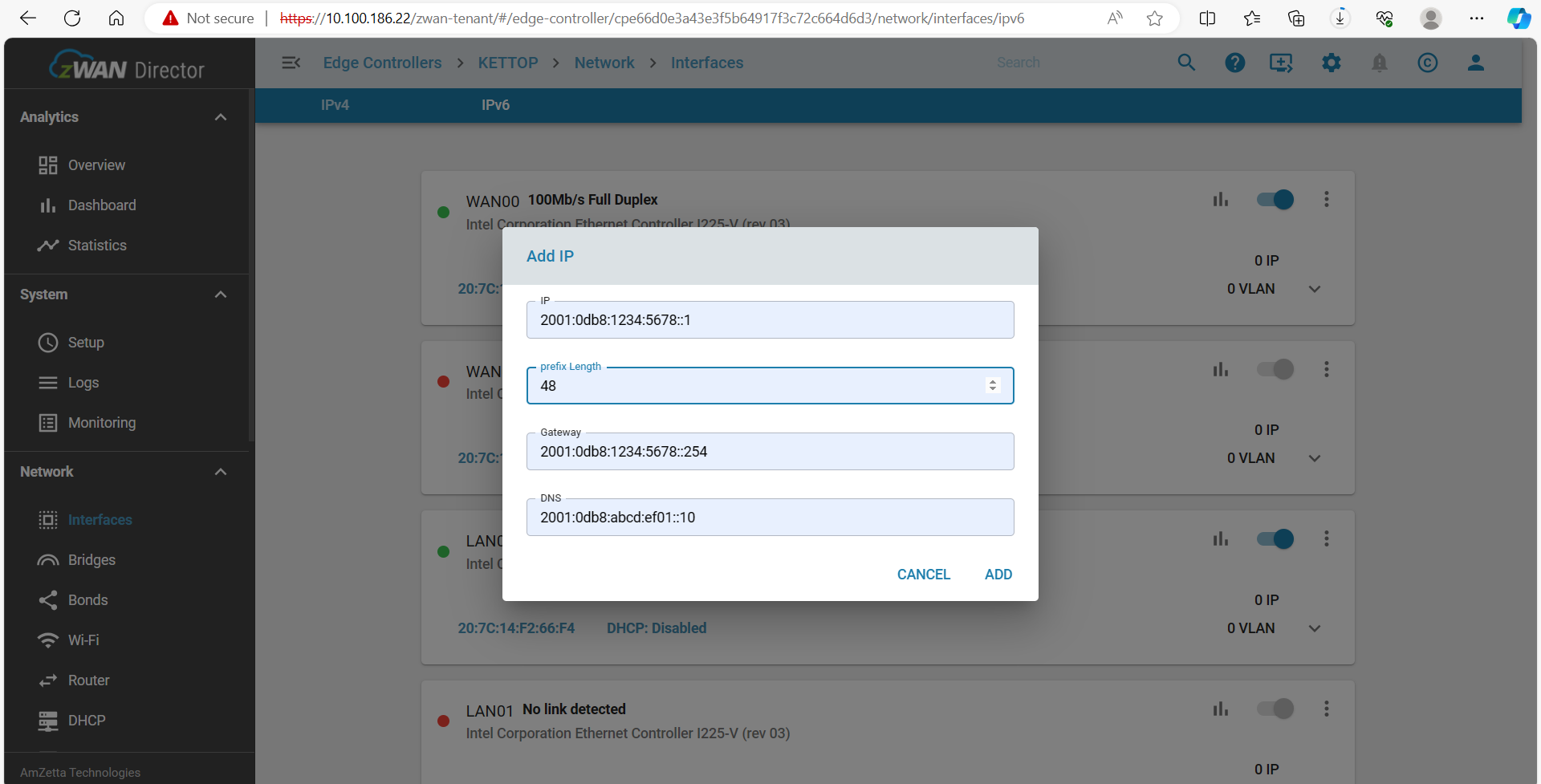
Assigning a Static IPv6 Address
To configure a static IP, specify the network IP and netmask. Once assigned, a unique ID will be generated, which is required for future modifications or deletions.
Using DHCP for IPv6
To dynamically acquire an IPv6 address, enable DHCP on the desired interface. Once obtained, you can renew or release the IP as needed.
Configuration Parameters
- Network IP: IPv6 Address to be assigned
- Netmask: Specifies the subnet
- UP/DOWN Interface: Enables or disables the interface
- TWAMP Responder: Determines if this interface participates in Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol (TWAMP) for network performance testing
Status Indicators
Interface status is displayed using color codes:
- GREEN: Interface is active and operational
- RED: Interface is down or unavailable
Use Cases
Network administrators can:
- Assign static or dynamic IPv6 addresses
- Connect to network devices via the assigned IP
- Establish VPN or IPsec tunnels on top of interfaces
IPv6 Benefits
IPv6 provides several key advantages over IPv4:
- 128-bit addressing: Ensures an almost limitless number of IP addresses
- Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC): Automatically configures devices on a network
- Built-in IPSec: Enhances security with integrated encryption
- Efficient packet processing: Reduces overhead by eliminating header checksums
- Improved multicast and anycast: Replaces IPv4’s broadcast method for better efficiency
Known Limitations
- IPv6 does not rely on NAT as IPv4 does, since its address space is much larger.
- Broadcast communication is replaced by more efficient multicast and anycast addressing.
Future Enhancements
- Enhanced Quality of Service (QoS) for better traffic prioritization
- Expanded interface data, including usage statistics and error reporting
- UI updates to indicate whether an interface is part of a bridge or bonded network