-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
- Firewall & Layer 7 Application Filtering
- VPN Site-to-Site Tunnel Setup & Connectivity (z40 to Cloud vGR)
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) / Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Testing
- DNS Filtering
- DDoS Protection & Logging
- MAC Address Filtering & Geo-fencing
- Application Control & Protocol Blocking
- Authentication & Access Control (zID)
-
- WAN Link Failover & Load Balancing (ACI Mode)
- Dynamic Path Selection & Application-Aware Routing
- SaaS & Internet Breakout Validation
- QoS for Microsoft Teams (Datacenter vGR + Branch z40)
- Tunnel Failover (z40 ↔ vGR) — WAN00 (wired) primary, WAN03 (4G) & WAN04 (5G) backups
- IP Routing & Static Route Steering (z40 Branch)
- VLAN & Layer-2 Bridging
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zTC
-
-
-
-
-
- Citrix HDX + USB Headset (Call-Center Baseline)
- VMware Horizon + Smart Card / CAC Login
- Microsoft AVD/RDP + Teams Optimized Video
- Multi-Monitor & 4K Performance
- USB Device Management - Block Storage
- Printing to Local USB & Network Printers
- Barcode Scanner (HID) with Line-of-Business App
- Kiosk / Assigned-Access Auto-Launch
- Wi-Fi Roaming & Link Change Mid-Session
- Power Management and Session State
- OS/Firmware Update & Rollback
-
-
StorTrends
-
zAccess
-
zGuardian
Stub Zone
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
DNS Stub Zone
A stub zone in zWAN CPE can be configured to point to an authoritative server for references to a specific zone. This can be a local or external DNS server that is directly reachable from the zWAN CPE. A stub zone is a copy of a zone that contains only the resource records necessary to identify the authoritative Domain Name System (DNS) servers for that zone. Stub zones help resolve names between separate DNS namespaces, which can be useful in scenarios such as corporate mergers or when integrating with an existing DNS server in an organization.
A stub zone consists of:
- The start of authority (SOA) resource record, name server (NS) resource records, and the glue A resource records for the delegated zone.
- The IP address of one or more master servers that update the stub zone. These servers are authoritative for the child zone and usually host the primary zone for the delegated domain name.
The stub zone maintains only the necessary information to contact the authoritative DNS servers, including NS records and A records required for resolution.
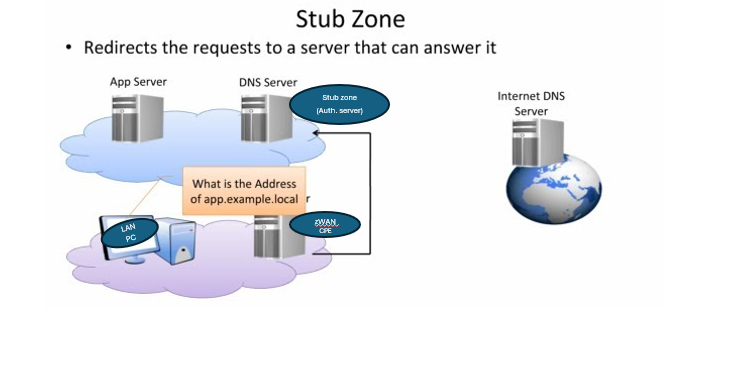
Differences Between Forward Zone, Auth Zone, and Stub Zone
- Stub Zone: Directs queries to an authoritative server to fetch information.
- Forward Zone: Sends queries to a recursive server to fetch information.
- Auth Zone: Loads a zone from a file and serves it locally or fetches information like an upstream server.
Process Overview
When a DNS client queries a DNS server hosting a stub zone, the server uses the stub zone’s resource records to resolve the query. The DNS server queries the authoritative DNS servers specified in the stub zone’s NS records. If these servers are unreachable, the DNS server attempts standard recursion using its root hints.
Functionality
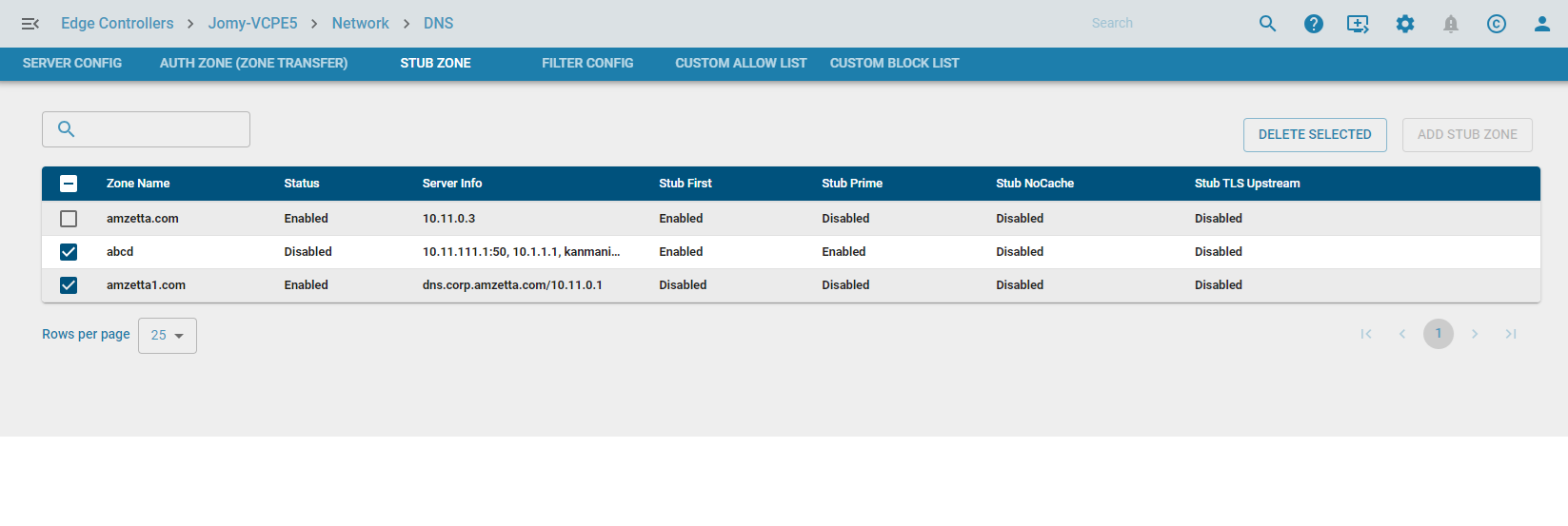
Stub zones can be configured in zWAN CPE using the Add Stub Zone functionality. Each stub zone must have a unique name, and multiple stub zones can be configured.
Parameters
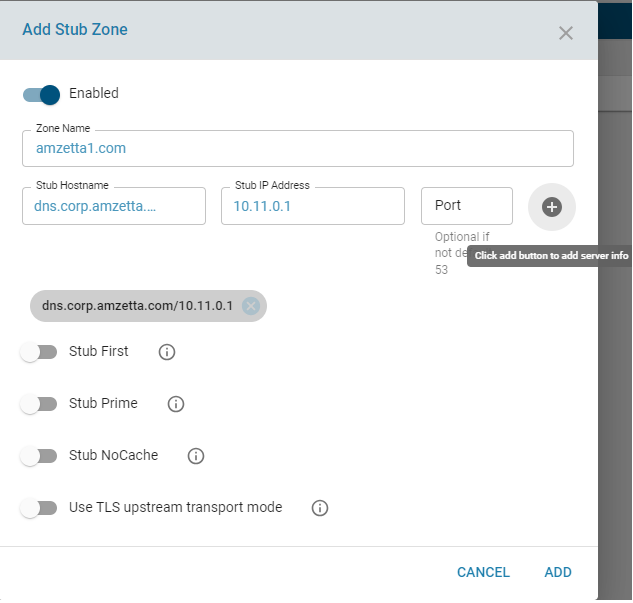
- serverInfo: IP/Hostname/Port of the authoritative server.
- stubFirst: (Default: Disabled) If enabled, retries without the stub clause if the query fails.
- stubPrime: (Default: Disabled) Performs NS set priming, similar to root hints.
- stubNoCache: (Default: Disabled) Prevents caching of stub zone data.
- stubTLSUpstream: (Default: Disabled) Enables TLS for stub queries.
Stub Zone Configuration
Add Stub Zone
Configures the CPE to refer to an authoritative DNS server for a specific zone.
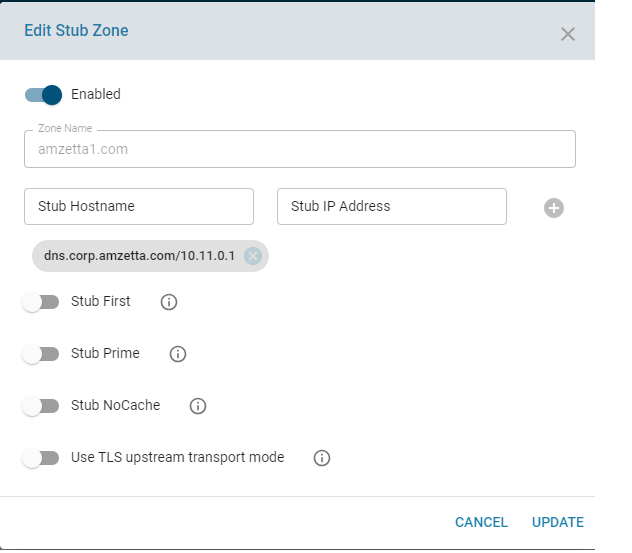
Edit Stub Zone
Allows modification of stub zone parameters or temporary disabling of a stub zone.
Delete Stub Zone
Removes one or multiple configured stub zones.
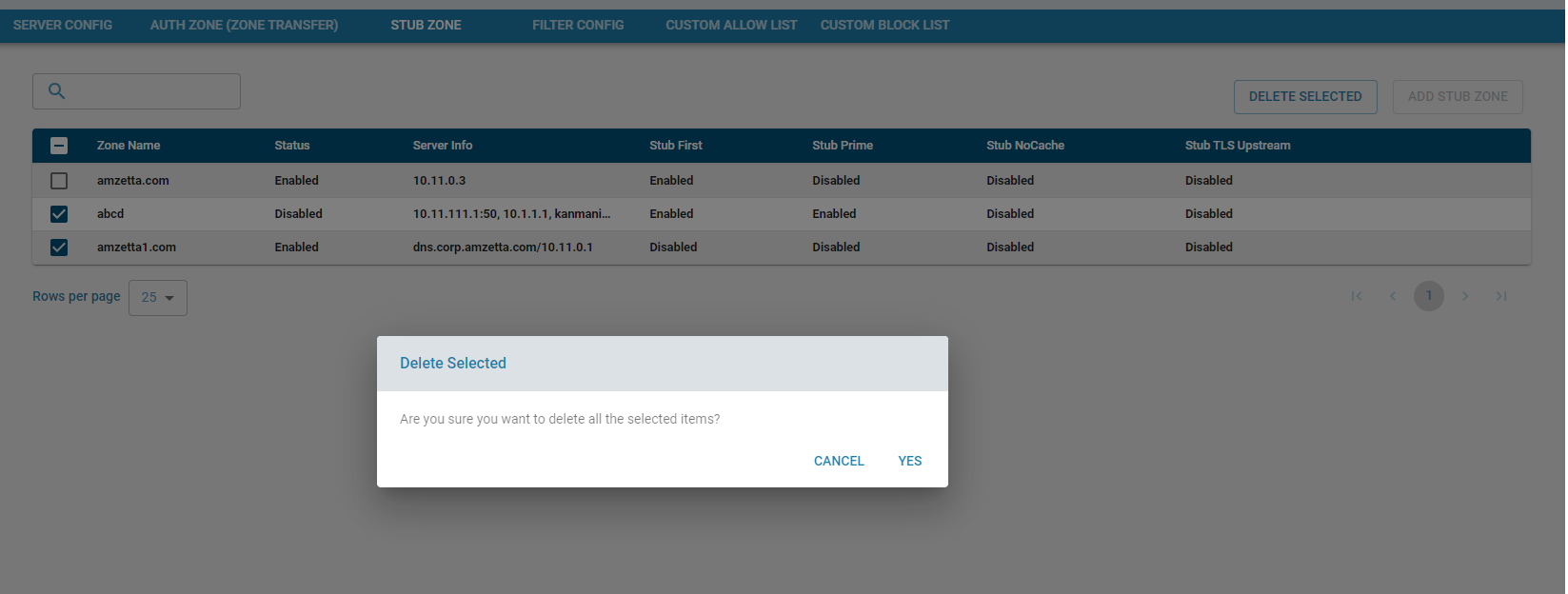
List Stub Zones
Displays all configured stub zones with search and sorting functionality.
References
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |