How can we help?
-
zWAN
-
-
-
-
- Firewall & Layer 7 Application Filtering
- VPN Site-to-Site Tunnel Setup & Connectivity (z40 to Cloud vGR)
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) / Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Testing
- DNS Filtering
- DDoS Protection & Logging
- MAC Address Filtering & Geo-fencing
- Application Control & Protocol Blocking
- Authentication & Access Control (zID)
-
- WAN Link Failover & Load Balancing (ACI Mode)
- Dynamic Path Selection & Application-Aware Routing
- SaaS & Internet Breakout Validation
- QoS for Microsoft Teams (Datacenter vGR + Branch z40)
- Tunnel Failover (z40 ↔ vGR) — WAN00 (wired) primary, WAN03 (4G) & WAN04 (5G) backups
- IP Routing & Static Route Steering (z40 Branch)
- VLAN & Layer-2 Bridging
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- IPsec Tunnel not Establishing
- SSL-VPN Tunnel not Establishing
- Mobile Network Issues
- Management Tunnel does not Establish
- DNS not Resolving from Local Network Appliance
- DNS Resolution Issues in Tunnel Configuration
- DHCP Server not Leasing IP to LAN PC
- Debugging EC Events - Unknown Status Issue
- Trusted-MAC Geofencing Issues
- DNS Issues from DC LAN PC
- Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity to Internet via WAN, Remote Branch LAN, or Local Branch LAN
- NetBalancer gateways displaying Faulty/Inactive
- Packet Drop Issues
-
-
zTC
-
-
-
-
-
- Citrix HDX + USB Headset (Call-Center Baseline)
- VMware Horizon + Smart Card / CAC Login
- Microsoft AVD/RDP + Teams Optimized Video
- Multi-Monitor & 4K Performance
- USB Device Management - Block Storage
- Printing to Local USB & Network Printers
- Barcode Scanner (HID) with Line-of-Business App
- Kiosk / Assigned-Access Auto-Launch
- Wi-Fi Roaming & Link Change Mid-Session
- Power Management and Session State
- OS/Firmware Update & Rollback
-
-
StorTrends
-
zAccess
-
zGuardian
You are here:
Print
Gateway
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
Overview
A gateway is a networking hardware component that acts as a crucial point for data movement within a network, connecting it to external networks and ensuring data routing across different network segments.
Functionality
The Gateway in the ZWAN controller provides essential routing capabilities with the following functionalities:
- Adding a Default Gateway – Define the default path for outbound traffic.
- Adding and Deleting Static Routes – Customize network paths for specific destinations.
- Listing Routes by Protocol – View routes managed through Auto, Static, OSPF, and BGP protocols.
- Enabling IP Forwarding – Allow routing between different network interfaces.
Configuration Parameters
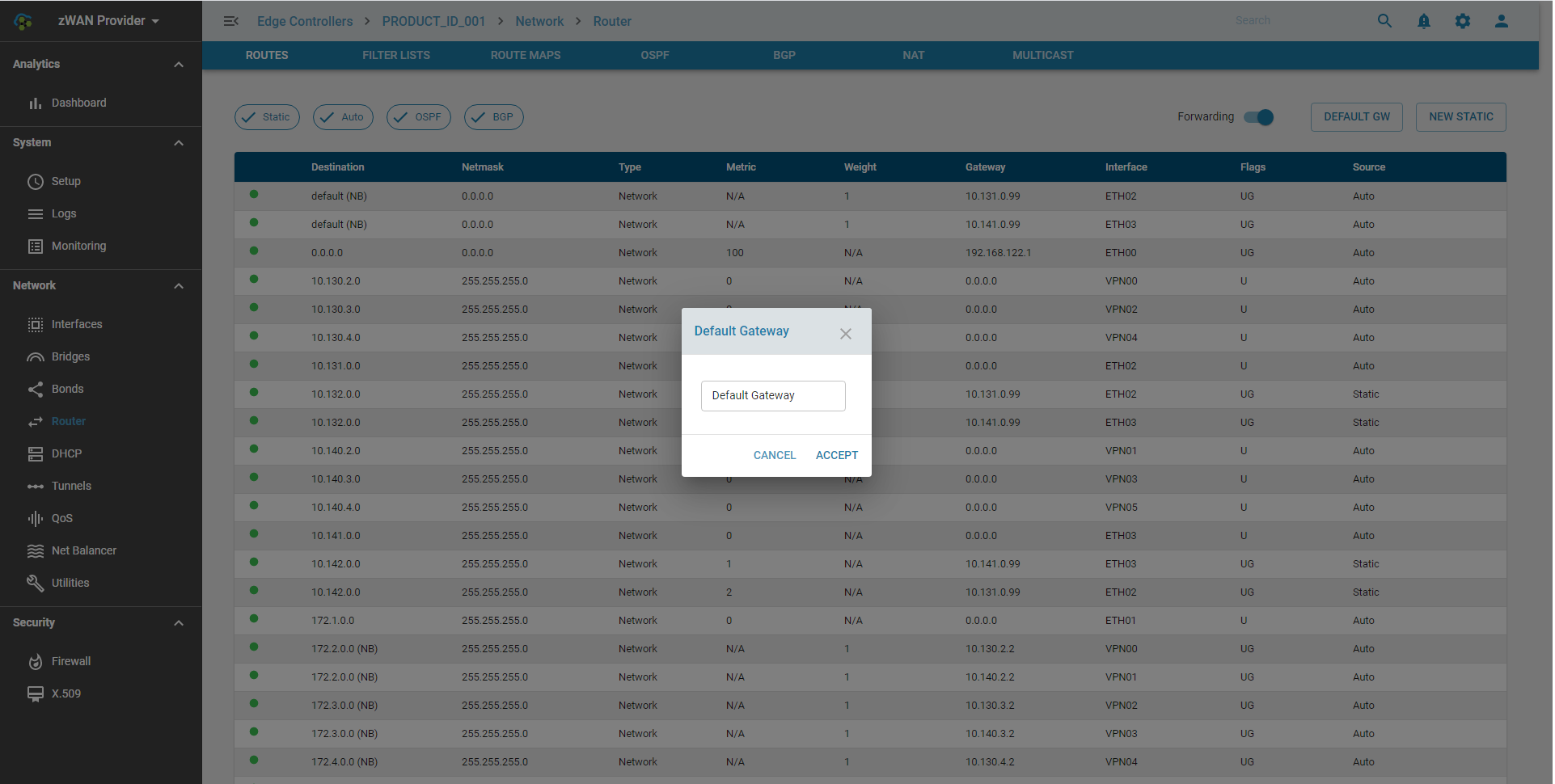
Adding a Default Gateway
Define the default path for network traffic when no specific route exists.
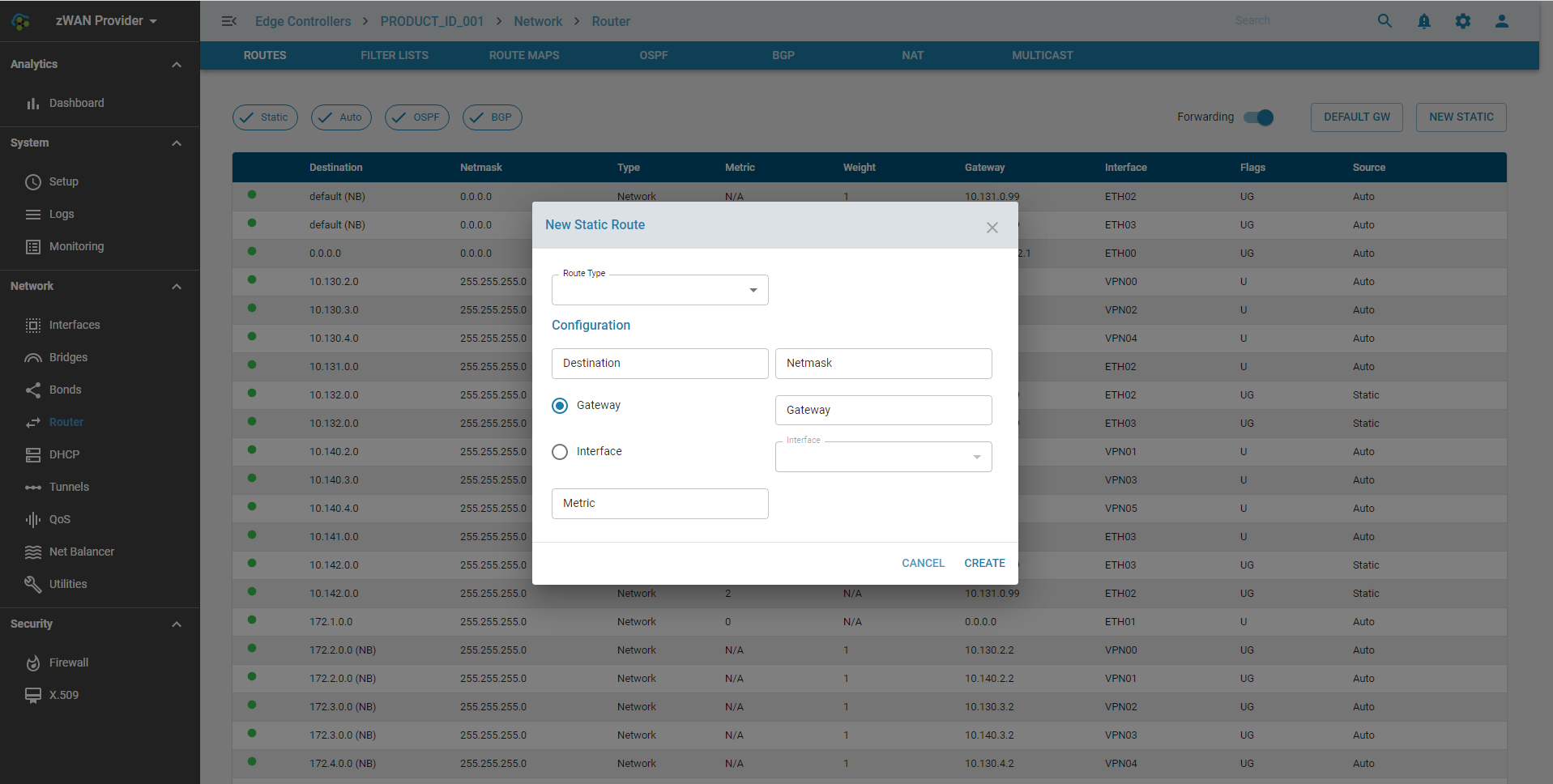
Adding a Static Route
Add custom static routes to manage traffic paths for specific network destinations.
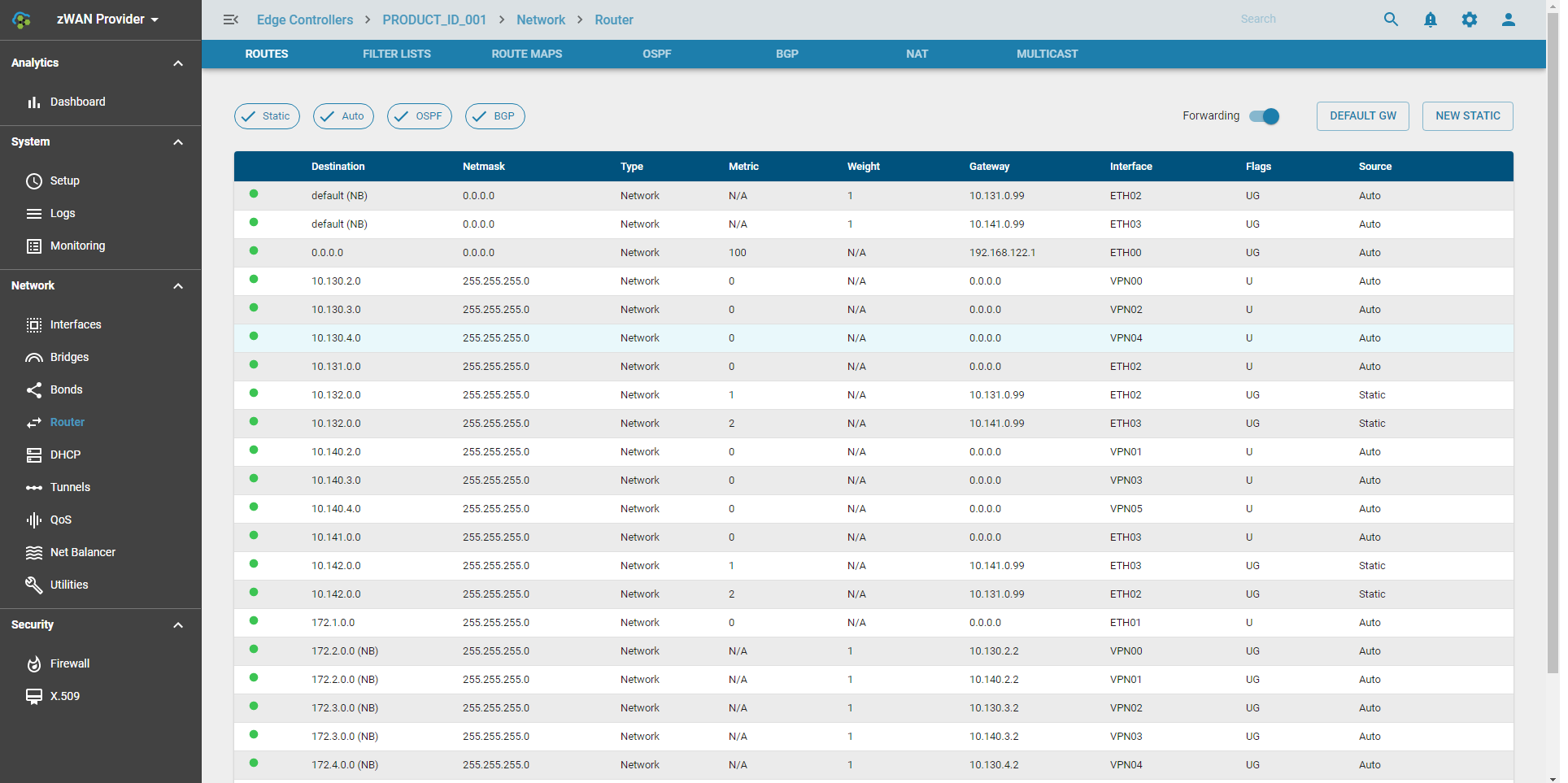
Listing Routes and Enabling IP Forwarding
Display routes across Auto, Static, OSPF, and BGP protocols, and configure IP Forwarding settings.
Use Cases
- Multi-WAN Setup – Set up different gateway routes for multi-WAN configurations.
- Custom Routing for Network Segmentation – Use static routes to direct traffic to specific segments within a network, enhancing security and traffic control.
- Optimized Path Management – Enable IP forwarding and protocol-based routing to improve data flow within complex networks.
Known Limitations
- Only 99 static routes can be created per zWAN controller.
Was this article helpful?
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
5
Table of Contents